The Power of Your Breath
Imagine you’re about to walk into a high-stakes interview. Your palms are sweaty, your heart is racing, and your mind is spiraling with doubt. Now, imagine taking a slow, deep breath — in for four counts, hold for four, out for four. Almost instantly, your body begins to settle. This simple shift is not magic — it’s biology in action.
Breath is often overlooked because it happens automatically. But what if you discovered that controlling your breath could be the fastest, most effective way to regulate your emotions, sharpen your mind, and even improve your physical health?
From elite athletes to meditation masters, people across the world use breathing techniques to anchor themselves, reduce stress, and boost performance. In fact, ancient practices like Pranayama and modern techniques like box breathing both show us that conscious breathing bridges the mind and body in transformative ways.
In this article, we’ll explore the science behind breath control, uncover how it influences the nervous system and emotions, introduce simple yet powerful breathwork techniques, and explain how this single practice can help you take back control of your life — one breath at a time.
The Science Behind Breath and the Nervous System
Breathing is the only bodily function that is both automatic and voluntary, which makes it uniquely powerful. You don’t have to think about it — yet you can change it at will. This gives you direct access to your body’s autonomic nervous system (ANS) — the system that controls your heart rate, digestion, blood pressure, and stress response.
Research shows that slow, controlled breathing can reduce cortisol levels — the primary stress hormone — while also improving heart rate variability (HRV), a marker of overall health and emotional resilience. Techniques like diaphragmatic breathing have been proven to reduce anxiety, lower blood pressure, and improve attention and focus.
Even the American Psychological Association acknowledges that deep breathing exercises are among the most effective strategies for stress relief. By taking control of your breath, you’re not just calming your mind — you’re literally shifting your body’s biology away from stress and into balance.
How Breath Affects the Mind and Emotions
Controlled breathing gives you a gateway to emotional regulation. When you slow your breath, you’re sending a signal to the brain — particularly the amygdala, the brain’s emotional processing center — that you’re safe. This reduces the intensity of emotional reactions and helps you respond more thoughtfully instead of reacting impulsively.
Numerous studies have shown that breathwork can decrease symptoms of anxiety and depression by balancing the nervous system and increasing mindfulness. In fact, breath-focused practices like mindfulness meditation often begin with anchoring your attention to the breath because it’s always in the present moment.
Breath control isn’t just for yogis and monks — it’s used in high-stress professions too. Navy SEALs are trained in “box breathing” to stay calm during combat. Athletes use breath control to improve focus and performance under pressure. Even public speakers and performers use deep breathing to calm nerves before going on stage.
Immediate Benefits of Breath Control
The most powerful changes often begin with the smallest shifts — and controlling your breath is one of the simplest yet most effective tools for immediate results. You don’t need hours of practice or fancy equipment. Just a few minutes of intentional breathing can create noticeable improvements in your body, mind, and overall energy.
Physical Benefits
According to the Cleveland Clinic, diaphragmatic breathing improves oxygen delivery throughout your body, promoting better digestion, enhancing lung function, and reducing physical tension — especially in the neck, shoulders, and jaw.
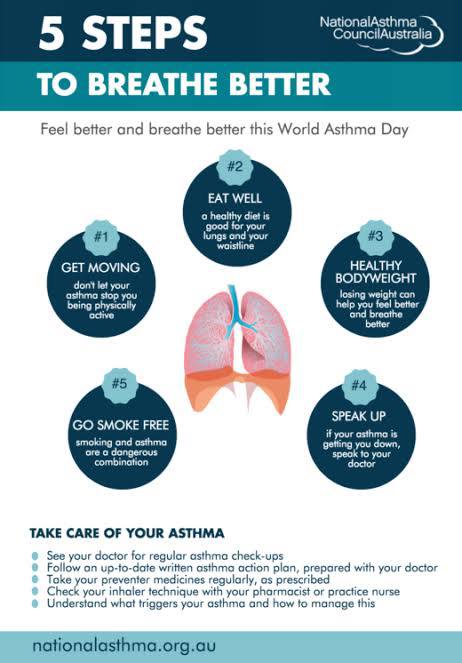
This infographic outlines five lifestyle steps — from staying active to quitting smoking — to improve breathing and asthma management. It also includes key tips for regular asthma care and medical check-ups.
Better breathing also contributes to improved sleep quality. Research has shown that slow breathing before bed can help people fall asleep faster and stay asleep longer by calming the nervous system and preparing the body for rest. It even supports your immune system by improving lymphatic flow and reducing inflammation.
Mental Benefits
The mental clarity that comes from conscious breathing is just as profound. When you regulate your breath, you’re enhancing blood flow to the brain, which helps you think more clearly and focus better. A study published in Frontiers in Human Neuroscience revealed that controlled breathing can significantly improve attention and memory.
Breathwork can also help you manage anxiety in real time. By engaging in practices like 4-7-8 breathing, you can calm a racing mind, soothe panic symptoms, and reset your internal rhythm. It’s like hitting the pause button on your stress.
Functional Benefits
In everyday life, better breathing leads to better performance. Whether you’re in a meeting, preparing for an exam, or navigating a tough conversation, a few conscious breaths can center you and improve your response. This isn’t just about relaxation — it’s about reclaiming your control in real-time situations.
Over time, these small daily moments of breath awareness compound, creating lasting changes in your productivity, mood, and overall quality of life. Your breath becomes more than an automatic function — it becomes your superpower.
Breathwork Techniques That Change Your Life
Below are five powerful and easy-to-learn breathwork techniques that can make an immediate impact on your mind and body.
Box Breathing (Square Breathing)
Box breathing is a method used by Navy SEALs to stay calm under pressure. It involves inhaling, holding, exhaling, and holding again — all for equal counts (typically 4 seconds each).
How to do it:
- Inhale for 4 seconds
- Hold for 4 seconds
- Exhale for 4 seconds
- Hold for 4 seconds
Repeat this cycle for 4–5 minutes.
2. 4-7-8 Breathing
Popularized by Dr. Andrew Weil, 4-7-8 breathing is a deeply relaxing technique that’s especially useful for reducing anxiety and improving sleep.
How to do it:
- Inhale through your nose for 4 seconds
- Hold your breath for 7 seconds
- Exhale slowly through your mouth for 8 seconds
Repeat for 4 cycles.
Alternate Nostril Breathing (Nadi Shodhana)
A classic practice in yoga, Nadi Shodhana helps balance energy and enhance mental clarity.
How to do it:
- Close your right nostril with your thumb and inhale through the left
- Close your left nostril with your ring finger and exhale through the right
- Inhale through the right, close it, and exhale through the left
That’s one cycle. Repeat for 5–10 cycles.
Deep Belly Breathing (Diaphragmatic Breathing)
Diaphragmatic breathing is one of the most fundamental techniques — and the foundation of all breathwork. It encourages full oxygen exchange and strengthens your diaphragm.
How to do it:
- Sit or lie down in a relaxed position
- Place one hand on your chest, one on your belly
- Breathe in slowly through your nose, feeling your belly rise
- Exhale through your mouth, feeling your belly fall
Practice for 5–10 minutes daily.
When and How to Use These Techniques
- Use box breathing before a presentation or during stressful tasks.
- Try 4-7-8 breathing at night to fall asleep faster.
- Practice alternate nostril breathing in the morning to feel balanced and refreshed.
- Incorporate deep belly breathing anytime you feel tension building.
- Use resonant breathing during breaks or before meditation for a sense of inner peace.
How Breath Control Empowers You in Daily Life
In Stressful Moments
According to the American Institute of Stress, controlled breathing can help shift you from reaction mode to response mode — creating space between stimulus and reaction. This not only improves your decision-making but also your relationships.
In Routine Tasks
Even the most mundane activities — commuting, cooking, waiting in line — become more mindful when you tune into your breath. Instead of allowing stress to build subconsciously, use these moments as micro-opportunities to practice breath awareness.

This visual explains Dr. Andrew Weil’s 4-7-8 breathing method, a simple technique to reduce stress and calm the nervous system. It guides users through a timed inhale, hold, and exhale cycle to improve mental and emotional balance.
For example, during your morning commute, try resonant breathing (inhale and exhale for 5 seconds each) to set a calmer tone for the day. While preparing meals, use deep belly breathing to stay present and grounded, rather than letting your mind wander into stress loops.
In Personal Growth
Breath control is also a powerful ally in long-term personal development. Whether you’re trying to break a bad habit, build emotional intelligence, or become more mindful, your breath becomes an anchor to bring you back to your goals.
Practices like mindfulness breathing are even being used in therapeutic settings to help people manage PTSD, depression, and trauma — proving that the breath is not just a tool for momentary calm, but for deep healing and growth.
Your Breath, Your Power
Whether you’re dealing with anxiety, burnout, decision fatigue, or even just daily stress, simple techniques like box breathing, 4-7-8 breathing, or diaphragmatic breathing can bring you back to yourself in a matter of minutes. These aren’t just temporary fixes — they are habit-forming tools that retrain your body and brain to respond more calmly and consciously to life.
The real magic lies in integration — using breath not just when you’re meditating or doing yoga, but while you’re working, walking, parenting, speaking, resting. When you practice breath awareness consistently, it becomes second nature, and life begins to feel less like something happening to you and more like something you’re actively shaping.
Frequently Asked Questions: Breath Control & Life Transformation
What is breathwork and how does it differ from regular breathing?
Breathwork is the practice of consciously controlling your breathing patterns to influence your physical, mental, and emotional state. Unlike unconscious breathing, breathwork involves intentional rhythms and techniques that activate specific responses in your nervous system.
Can controlling my breath really help me control my life?
Yes, because your breath directly affects your heart rate, stress levels, focus, and mood. By mastering your breath, you gain control over your body’s stress response, allowing you to make clearer decisions and respond rather than react.
How quickly can I feel the effects of breathwork?
Many people report feeling calmer and more focused within just a few minutes. Techniques like box breathing or 4-7-8 breathing can lower your heart rate and ease anxiety almost instantly.
Do I need any equipment to start breathwork?
No. You only need your body and a few quiet minutes. Breathwork is one of the most accessible wellness practices because it requires no tools or external aids.
Which breathing technique is best for anxiety?
The 4-7-8 technique is especially helpful for anxiety because the extended exhale activates the parasympathetic nervous system, helping you feel calmer and grounded.
Is breathwork scientifically proven?
Yes, numerous studies have confirmed that controlled breathing improves heart rate variability, reduces cortisol levels, enhances focus, and lowers blood pressure. It’s used in clinical therapy, athletic training, and meditation practices.
Can breathwork improve my sleep?
Absolutely. Practicing deep breathing or 4-7-8 breathing before bed slows down your nervous system and prepares your body for restful sleep.
How does breath control affect the brain?
Controlled breathing increases oxygen delivery to the brain, improves mental clarity, and enhances cognitive function. It also helps regulate emotions by calming the amygdala, the brain’s fear center.
Can breathwork help me manage anger or frustration?
Yes. Slowing your breath reduces the intensity of emotional reactions and helps you shift from fight-or-flight mode into a calmer, more thoughtful state.
Is breathwork the same as meditation?
Breathwork can be a form of meditation, but it’s also effective on its own. You can practice breath control without entering a meditative state, and it can still deliver benefits like calmness and focus.
How long should I practice breathwork each day?
Even just 5 minutes a day can be transformative. However, the ideal range is 5 to 15 minutes daily for long-term benefits. Consistency is more important than duration.
Can I do breathwork while walking or working?
Yes. You can use breath awareness during routine activities to stay calm and focused. Techniques like resonant breathing are great for walking, working, or commuting.
What’s the best time of day to practice breathwork?
Morning breathwork sets a positive tone for the day, while evening breathwork helps you relax and sleep better. Choose a time that fits your schedule and energy levels.
Can breathwork help with focus and productivity?
Definitely. Breath control increases oxygen flow to the brain and reduces mental clutter, which boosts concentration and productivity — especially during long work sessions.
Is it safe to do breathwork daily?
Yes, daily breathwork is safe for most people. However, people with certain medical conditions (e.g., respiratory issues or heart conditions) should consult a doctor before starting intensive techniques.
What is the difference between nasal and mouth breathing in breathwork?
Nasal breathing is preferred in most breathwork practices because it filters, humidifies, and warms the air. It also activates the diaphragm more effectively, promoting relaxation.
Can children or elderly people do breathwork?
Yes, breathwork can be adapted for all ages. Simple techniques like deep belly breathing are safe and beneficial for both children and older adults.
Does breathwork have spiritual benefits?
Many people experience deeper self-awareness and inner peace through breathwork. In spiritual traditions like yoga and Buddhism, breath is considered a bridge between body and spirit.
Can breath control improve athletic performance?
Yes. Breathwork improves oxygen efficiency, endurance, and recovery. Athletes use techniques like diaphragmatic breathing to stay calm and focused under pressure.
How do I stay motivated to practice breathwork every day?
Start small, track how you feel after each session, and attach it to a daily habit like brushing your teeth or making coffee. As you begin to notice results, motivation will come naturally.
– Authored by Mridu Mishra





