Hormonal Issues in Women have become increasingly prevalent due to modern lifestyle stressors, poor dietary habits, environmental toxins, and inadequate sleep. These imbalances can manifest as irregular periods, weight fluctuations, chronic fatigue, mood swings, anxiety, and fertility issues. Common conditions associated with hormonal disruptions include polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), thyroid disorders, adrenal fatigue, and estrogen dominance.
One of the primary drivers of hormonal issues in women is chronic stress, which elevates cortisol levels and disrupts the delicate balance of estrogen, progesterone, and thyroid hormones. This can lead to missed or painful periods, mood disorders, and metabolic dysfunction. Poor nutrition, including excessive sugar and processed foods, contributes to insulin resistance, inflammation, and hormonal dysregulation. Sleep deprivation and exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) in plastics, cosmetics, and processed foods further exacerbate the issue.
While physiological factors play a significant role, the psychological dimension- particularly stress and emotional well-being, has emerged as a critical contributor to these hormonal disturbances.
It’s important to understand the intricate relationship between psychological factors and hormonal health in women.
Hormonal Issues in Women: The Interplay Between Stress and Hormonal Imbalance
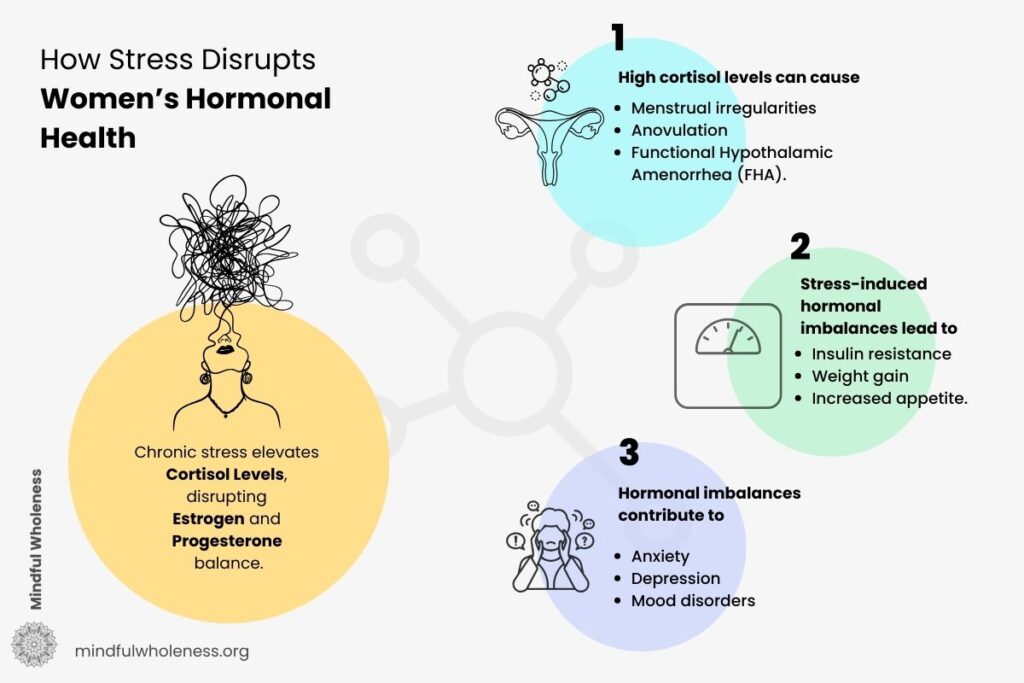
Chronic stress has been identified as a pivotal factor creating hormonal issues in women. The body’s response to prolonged stress involves the sustained release of cortisol and adrenaline, hormones that, when persistently elevated, can lead to significant hormonal imbalances. This disruption affects various bodily functions, including reproductive health, metabolic processes, and overall well-being.
- Impact on Reproductive Health: Prolonged stress can lead to elevated cortisol levels, which may disrupt the balance of reproductive hormones such as estrogen and progesterone. This imbalance can result in menstrual irregularities, anovulation, and conditions like functional hypothalamic amenorrhea (FHA).
- Metabolic Consequences: Chronic stress-induced hormonal imbalances can contribute to metabolic issues, including weight gain and insulin resistance. Elevated cortisol levels are associated with increased appetite and fat deposition, particularly in the abdominal region, which heightens the risk of metabolic disorders.
- Mental Health Implications: The bidirectional relationship between stress and hormonal imbalance suggests that not only can stress lead to hormonal disturbances, but these imbalances can also exacerbate mental health conditions such as anxiety and depression. Fluctuations in hormones like estrogen and progesterone are linked to mood changes and increased susceptibility to mood disorders.
Psychological Factors Contributing to Hormonal Issues in Women
Beyond general stress, certain psychological factors are closely associated with specific hormonal issues in women.
- Functional Hypothalamic Amenorrhea (FHA): FHA is characterized by the absence of menstrual periods due to hypothalamic suppression, often triggered by stress, significant weight loss, or excessive exercise. Psychological factors such as depression, anxiety, and a strong drive for thinness are prevalent among women with FHA. These mental health challenges can lead to behaviors that further disrupt hormonal balance, creating a vicious cycle.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): PCOS is a common endocrine disorder marked by irregular menstrual cycles, hyperandrogenism, and polycystic ovaries. While the exact etiology is multifactorial, stress and psychological distress can exacerbate PCOS symptoms. The chronic stress response may influence insulin resistance and androgen levels, worsening the clinical presentation of PCOS.
- Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder (PMDD): PMDD is a severe form of premenstrual syndrome characterized by significant mood disturbances. Women with PMDD exhibit heightened sensitivity to normal hormonal fluctuations, leading to pronounced emotional and physical symptoms. Psychological stress can intensify these symptoms, suggesting a complex interaction between hormonal changes and emotional regulation.
Mechanisms Linking Psychological Stress to Hormonal Issues in Women
Understanding the pathways through which psychological stress affects hormonal balance is crucial for developing effective interventions.
- Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal (HPA) Axis Activation: Chronic psychological stress activates the HPA axis, leading to increased secretion of cortisol. Elevated cortisol levels can suppress the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis, disrupting the production of reproductive hormones and leading to menstrual irregularities and fertility issues.
- Neurotransmitter Interactions: Stress influences neurotransmitter systems, including serotonin and dopamine, which play roles in mood regulation and hormonal control. Alterations in these neurotransmitters can affect the release of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), subsequently impacting the menstrual cycle and ovarian function.
- Behavioral Responses to Stress: Psychological stress can lead to behaviors such as disordered eating, excessive physical activity, or substance use, which can further disrupt hormonal balance. For instance, restrictive eating patterns associated with stress can lead to energy deficits, impairing reproductive hormone production and leading to conditions like FHA.
Implications for Treatment and Management for Hormonal Issues in Women:
Addressing the psychological components of hormonal imbalances is essential for effective treatment and management of hormonal issues in women.
- Integrative Therapeutic Approaches: Combining psychological interventions with medical treatments can enhance outcomes for women experiencing hormonal imbalances. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), stress management techniques, and mindfulness-based therapies can alleviate psychological distress, potentially restoring hormonal equilibrium.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Encouraging regular physical activity, balanced nutrition, and adequate sleep can mitigate the effects of stress on hormonal health. These lifestyle factors play a crucial role in maintaining hormonal balance and overall well-being .
- Education and Awareness: Empowering women with knowledge about the interplay between psychological health and hormonal balance can promote proactive health behaviors. Understanding the signs of hormonal imbalances and their potential psychological triggers enables women to seek timely and appropriate care.
Health Plan for Managing Hormonal Issues in Modern Women
Hormonal imbalances can lead to conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), thyroid disorders, adrenal fatigue, and menstrual irregularities. Addressing these issues requires a holistic approach that encompasses dietary modifications, stress management, regular physical activity, and mindful lifestyle choices.
Nutritional Strategies for Hormonal Balance
Diet plays a pivotal role in regulating hormones. Consuming a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients supports endocrine function and promotes overall well-being.
- Incorporate Healthy Fats: Healthy fats are essential for hormone production and balance. Including sources such as avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil in your diet can support the synthesis of hormones involved in appetite regulation, metabolism, and satiety.
- Prioritize Fiber Intake: Fiber plays a crucial role in maintaining hormonal balance by aiding digestion and regulating blood sugar levels. Consuming a variety of fiber-rich foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, can support overall hormonal health.
- Opt for Lean Proteins: Proteins are the building blocks of hormone production. Incorporating lean protein sources such as poultry, fish, legumes, and plant-based options like tofu and tempeh can provide the necessary amino acids for hormone synthesis.
- Stay Hydrated: Adequate hydration is essential for optimal cellular function, including hormone transport and metabolism. Aim to drink at least eight glasses of water daily to support overall health and hormonal balance.
Stress Management Techniques
Chronic stress disrupts the body’s hormonal equilibrium, leading to imbalances that affect mood, metabolism, and reproductive health. Implementing effective stress management strategies is crucial for maintaining hormonal harmony.
- Engage in Regular Physical Activity: Regular exercise positively influences hormone regulation. Activities such as strength training and high-intensity interval training (HIIT) can boost hormone levels, including growth hormone and testosterone, which are vital for muscle growth and overall health.
- Practice Mindfulness and Meditation: Mindfulness practices, including meditation and deep breathing exercises, can help reduce stress and lower cortisol levels. Incorporating these practices into your daily routine can promote relaxation and support hormonal balance.
- Establish Healthy Sleep Habits: Quality sleep is essential for hormonal regulation. Aim for 7-9 hours of uninterrupted sleep each night, and create a sleep-friendly environment by keeping your bedroom dark, quiet, and cool.
Physical Activity and Hormonal Health
Engaging in regular physical activity is vital for maintaining hormonal balance. Exercise influences the release and regulation of various hormones, contributing to improved mood, metabolism, and reproductive health.
- Incorporate Strength Training: Strength training exercises, such as weightlifting, can enhance muscle mass and boost metabolism. This form of exercise stimulates the release of hormones like testosterone and growth hormone, which are essential for muscle development and overall vitality.
- Engage in Cardiovascular Exercise: Aerobic activities, including walking, running, and cycling, can improve cardiovascular health and support hormonal balance. Regular cardio exercise helps regulate insulin levels and reduces the risk of metabolic disorders.
- Practice Yoga and Stretching: Incorporating yoga and stretching routines can enhance flexibility, reduce stress, and promote relaxation. These practices support the parasympathetic nervous system, aiding in the reduction of cortisol levels and fostering hormonal equilibrium.
Lifestyle Modifications for Hormonal Balance
Adopting specific lifestyle changes can significantly impact hormonal health. Mindful choices in daily habits contribute to the maintenance of hormonal equilibrium.
- Maintain a Healthy Body Weight: Achieving and sustaining a healthy weight is crucial for hormonal balance. Excess body fat, particularly around the abdomen, can disrupt hormone levels and increase the risk of conditions like insulin resistance and estrogen dominance.
- Limit Exposure to Endocrine Disruptors: Reducing exposure to environmental toxins, such as certain household cleaners and personal care products containing harmful chemicals, can help maintain hormonal health. Opt for natural and organic products to minimize the intake of endocrine-disrupting substances.
- Avoid Excessive Light Exposure at Night: Exposure to artificial light during nighttime hours can interfere with the body’s natural circadian rhythm and suppress melatonin production, leading to sleep disturbances and hormonal imbalances. Limiting screen time and using dim lighting in the evening can support better sleep quality and hormonal health.
Medical Consultation and Monitoring for Hormonal Issues in Women
Regular medical check-ups and consultations with healthcare professionals are essential for monitoring hormonal health and addressing any imbalances effectively.
- Seek Professional Guidance: If you experience symptoms indicative of hormonal imbalances, such as irregular menstrual cycles, unexplained weight changes, persistent fatigue, or mood fluctuations, consult a healthcare provider specializing in endocrinology or women’s health. Early intervention can prevent potential complications and promote overall well-being.
- Consider Hormonal Assessments: Under the guidance of a healthcare professional, hormonal assessments can help identify specific imbalances and inform personalized treatment plans. These assessments may include blood tests to measure levels of key hormones such as estrogen, progesterone, testosterone, and thyroid hormones.
The rising incidence of hormonal issues in women cannot be fully addressed without considering the profound impact of psychological factors. Chronic stress, mental health disorders, and behavioral responses significantly contribute to hormonal dysregulation, affecting reproductive, metabolic, and emotional health.
A comprehensive approach that integrates psychological well-being with medical care is imperative for effectively managing and preventing hormonal imbalances in women. Maintaining hormonal balance is integral to a woman’s overall health and quality of life.
By implementing a comprehensive approach that includes a nutrient-rich diet, effective stress management techniques, regular physical activity, mindful lifestyle choices, and proactive medical consultation, women can support their hormonal health and enhance their well-being. For personalized advice and treatment options, it is recommended to consult with healthcare professionals who can provide tailored guidance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) on Hormonal Issues in Women and Mental Health
- What is hormonal imbalance, and how does it affect women?
Hormonal imbalance occurs when there is too much or too little of a hormone in the bloodstream, disrupting normal bodily functions. In women, this can lead to irregular menstrual cycles, fertility issues, weight fluctuations, mood disorders, and chronic fatigue. Research suggests that stress, anxiety, and depression significantly impact hormone regulation, contributing to conditions like PCOS, thyroid dysfunction, and adrenal fatigue.
- Can stress cause hormonal imbalances in women?
Yes, chronic stress is a major contributor to hormonal imbalances. The constant release of cortisol (the stress hormone) interferes with the production of estrogen, progesterone, and thyroid hormones, leading to menstrual irregularities, mood swings, and metabolic disruptions. Studies confirm that women under high stress levels are more likely to develop reproductive and endocrine disorders
- What are the most common hormonal disorders caused by psychological stress?
The most common stress-related hormonal disorders in women include:- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) – Linked to chronic stress, insulin resistance, and elevated androgens.
- Thyroid Dysfunction – Stress affects thyroid hormone production, leading to hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism.
- Functional Hypothalamic Amenorrhea (FHA) – Severe stress suppresses reproductive hormones, causing missed periods and infertility.
- Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder (PMDD) – An extreme form of PMS where stress exacerbates hormonal fluctuations and mood disturbances .
- What role do neurotransmitters play in hormonal balance?
Neurotransmitters like serotonin, dopamine, and GABA regulate mood and also influence hormonal production. When stress or anxiety alters neurotransmitter levels, it disrupts the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, affecting reproductive and metabolic hormones. This is why women with depression and anxiety often experience irregular cycles and hormonal imbalances.
- How does anxiety impact female hormones?
Anxiety leads to excess cortisol production, which disrupts estrogen, progesterone, and thyroid hormone levels. This can result in menstrual irregularities, increased PMS symptoms, and fertility problems. Women with generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) or panic disorders often report more severe hormonal symptoms compared to those without anxiety.
- Can depression cause hormonal imbalances?
Yes, depression can alter the balance of estrogen, progesterone, and cortisol, affecting mood, metabolism, and reproductive health. Studies indicate that women with major depressive disorder have irregular cortisol rhythms, which impact their menstrual cycles and thyroid function.
- Does lack of sleep affect hormone levels in women?
Yes, poor sleep increases cortisol while reducing melatonin, estrogen, and progesterone, leading to fatigue, mood swings, and metabolic dysfunction. Sleep deprivation is linked to higher rates of PCOS, thyroid dysfunction, and insulin resistance. Women who sleep less than six hours a night are more likely to have hormonal imbalances
- How does diet impact hormonal health in women?
A diet high in processed foods, sugar, and unhealthy fats can trigger inflammation, insulin resistance, and hormonal disruptions. Studies show that eating whole foods rich in fiber, healthy fats, and phytoestrogens (found in flaxseeds and soy) helps regulate estrogen levels and supports reproductive health (nutrition.org, 2020 ).
- Can excessive exercise lead to hormonal problems?
Yes, intense physical activity without proper recovery can elevate cortisol levels, leading to missed periods, decreased estrogen, and chronic fatigue. Overtraining is particularly common among women with a history of disordered eating and high-stress levels. Studies recommend moderate exercise combined with proper nutrition to maintain hormonal balance.
- Does gut health affect hormone balance?
Yes, the gut microbiome plays a crucial role in metabolizing estrogen. An imbalance in gut bacteria (dysbiosis) can lead to estrogen dominance, weight gain, and menstrual irregularities. Consuming probiotics, prebiotics, and fiber-rich foods supports healthy estrogen metabolism and hormonal balance
- How can stress management help regulate hormones?
Reducing stress through meditation, mindfulness, yoga, and breathing exercises lowers cortisol levels, which helps balance estrogen, progesterone, and thyroid hormones. Studies show that mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) programs significantly improve hormonal function in women with PCOS and thyroid disorders.
- Can therapy improve hormonal imbalances?
Yes, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) has been shown to regulate stress hormones like cortisol, improving menstrual regularity and reducing symptoms of PMDD. Women undergoing CBT for anxiety and depression report better reproductive health outcomes and improved thyroid function.
- Are natural remedies effective for hormonal balance?
Certain natural remedies, such as ashwagandha, maca root, and vitex (chasteberry), have been found to support hormonal balance by regulating cortisol and estrogen levels. However, their effectiveness varies, and they should be used under medical supervision. Research shows that ashwagandha lowers cortisol and helps balance adrenal function in women with chronic stress.
- What are the warning signs of severe hormonal imbalance?
Women should seek medical help if they experience:- Severe menstrual irregularities (missing periods for months)
- Unexplained weight gain or loss
- Chronic fatigue and brain fog
- Persistent mood swings, anxiety, or depression
- Hair loss, excessive facial hair, or skin issues (acne, dryness)
- What medical tests diagnose hormonal imbalances?
Doctors may order tests such as:- Hormone panels (estrogen, progesterone, testosterone, thyroid, cortisol)
- Blood sugar and insulin resistance tests
- Ultrasounds for PCOS diagnosis
- What treatments are available for hormonal imbalances?
Treatments may include:- Lifestyle changes (diet, exercise, stress reduction)
- Hormonal therapies (birth control, thyroid medication, bioidentical hormones)
- Medications for insulin resistance (metformin) or adrenal dysfunction