Mindfulness: The Everyday Superpower Hiding in Plain Sight
Many people mistakenly believe that mindfulness is boring, tedious, or just another wellness trend that requires sitting still and doing “nothing.” However, this perception couldn’t be further from the truth.
In reality, mindfulness is a powerful mental skill that can transform the way your brain functions and enhance your overall well-being. If you think mindfulness is dull, you’re not alone — but science and experience tell a different story.
Mindfulness is defined as the practice of paying purposeful, non-judgmental attention to the present moment, and it has roots in ancient meditation traditions but has gained widespread popularity in modern psychology and neuroscience. Far from being boring, it actively engages your brain’s ability to focus, regulate emotions, and increase self-awareness.
According to research published by Harvard Medical School, mindfulness training literally changes brain structure and function, making it a “superpower” for cognitive control and emotional resilience.
In today’s fast-paced and distraction-heavy world, mindfulness offers a much-needed antidote. Instead of zoning out or feeling overwhelmed by constant multitasking, mindfulness teaches your brain to slow down, sharpen focus, and improve mental clarity.
A study supported by the NIH highlights how mindfulness meditation strengthens attention and cognitive flexibility. This mental training is supported by decades of scientific evidence demonstrating benefits such as reduced stress, better attention span, and enhanced emotional regulation.
This article will explore how mindfulness is far from boring and why it’s actually one of the most effective superpowers you can develop for your brain.
What Is Mindfulness?
Mindfulness is often misunderstood, so it’s important to start with a clear and practical explanation. At its core, mindfulness means paying attention deliberately and non-judgmentally to the present moment.
Unlike daydreaming or zoning out, mindfulness involves an active awareness of your thoughts, feelings, bodily sensations, and surrounding environment. You can explore a detailed definition of mindfulness on Mindful.org, which highlights how this practice cultivates a calm and focused mind.
The practice of mindfulness has its roots in ancient Buddhist meditation but has since been adapted and embraced by modern science and psychology as a secular tool to improve mental health. The history of mindfulness shows how this ancient tradition has evolved to become a mainstream therapeutic approach, with programs like Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR) gaining global recognition.
Today, mindfulness is widely used in clinical settings to help manage conditions such as anxiety, depression, and chronic pain, as supported by research from Johns Hopkins Medicine.
Mindfulness can take many forms beyond the typical seated meditation. For example, mindful breathing is a simple yet powerful practice where you focus your attention on the rhythm of your breath, noticing each inhale and exhale.
Similarly, mindful walking encourages you to bring awareness to the sensations of movement and your surroundings, making everyday walking a meditative experience.
Even daily routines such as eating can be transformed through mindful eating techniques that invite you to savor every bite and notice flavors, textures, and smells in the present moment.
A fundamental aspect that sets mindfulness apart is its emphasis on non-judgmental awareness. This means observing your experience without labeling thoughts or emotions as good or bad, which helps reduce stress and promotes self-compassion.
Contrary to popular belief, mindfulness is not about clearing your mind or suppressing thoughts but about being fully present with whatever arises. Psychologists clarify these common myths about mindfulness meditation, helping beginners understand that it’s okay for the mind to wander, as long as you gently bring your focus back.
For those interested in exploring mindfulness further, many digital tools and resources make it accessible. Popular apps like Headspace and Calm offer guided meditations and daily mindfulness exercises suited for all levels.
Books such as Wherever You Go, There You Are by Jon Kabat-Zinn provide deep insight into the practice and philosophy of mindfulness and can be found easily online. Additionally, local mindfulness groups, online courses, and retreats offer supportive environments to develop your practice more deeply.
By understanding what mindfulness truly is, you can see why it is far from boring—it is an active, engaging process that trains your brain to live fully in the present moment, enhancing both mental clarity and emotional balance.
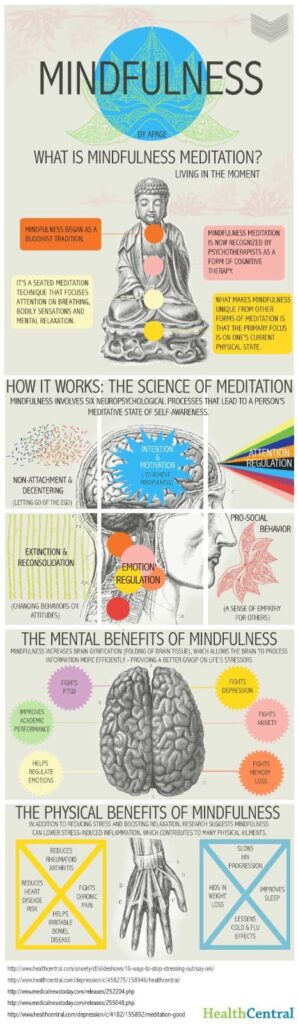
This infographic visually explains how mindfulness meditation works by highlighting its effects on the brain and emotional regulation. It supports the idea that mindfulness isn’t boring—it’s a powerful tool that rewires the brain for focus, calm, and self-awareness.
Why Do People Think Mindfulness Is Boring?
Despite its proven benefits, many people hesitate to try mindfulness because they believe it is boring or dull. This common misconception is fueled by cultural stereotypes and media portrayals that often depict mindfulness and meditation as slow, monotonous activities reserved for spiritual monks or those with a lot of free time.
Mainstream media sometimes presents mindfulness as a niche or esoteric practice, which can make it seem inaccessible or irrelevant to everyday life. Articles in popular culture occasionally describe mindfulness as just “sitting quietly” or “emptying your mind,” which can sound unappealing to people used to fast-paced, action-oriented lifestyles.
These misconceptions are explored in depth in Harvard Business Review’s discussion on mindfulness myths.
Another reason mindfulness is seen as boring is the challenge it presents in our modern, distraction-filled world. With constant notifications, social media, and multitasking becoming the norm, slowing down to focus on the present moment feels counterintuitive or even uncomfortable for many.
The struggle to sit still and “do nothing” can be frustrating, especially for those new to the practice. This is why some people abandon mindfulness quickly, thinking it doesn’t suit their personality or lifestyle. The American Psychological Association discusses how the difficulty in adopting mindfulness practices can be discouraging without proper guidance.
Moreover, the idea that mindfulness requires long, silent meditation sessions can deter busy individuals who believe they don’t have the time or patience. The misconception that mindfulness is an all-or-nothing practice ignores the wide variety of accessible, brief exercises that can be incorporated into daily life.
Research from NHS Mindfulness emphasizes that even short mindfulness moments, such as a few deep breaths or a brief body scan, can be highly effective without being boring or time-consuming.
Finally, some critics argue that mindfulness has become overly commercialized, with apps, books, and courses marketed in ways that feel superficial or gimmicky. This commercialization can contribute to skepticism, making people doubt the authenticity and value of mindfulness.
However, well-designed programs based on rigorous scientific research, such as Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT), demonstrate the genuine power and versatility of mindfulness beyond the hype.
In summary, the perception of mindfulness as boring is shaped by misconceptions about what the practice entails, societal attitudes toward stillness and slowing down, and a lack of awareness of the diverse ways mindfulness can be integrated into busy lives. Understanding these barriers is the first step to overcoming them and discovering how engaging and transformative mindfulness truly is.
The Neuroscience Behind Mindfulness — Why It’s a Brain Superpower
Mindfulness is often described as a superpower for your brain because of its profound effects on brain structure and function. Neuroscience research reveals that regular mindfulness practice promotes neuroplasticity, the brain’s ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections throughout life.
This means that through mindfulness, you can literally reshape your brain to become more resilient, focused, and emotionally balanced, as explained by experts at Frontiers in Human Neuroscience.
One of the key areas affected by mindfulness is the prefrontal cortex, which governs executive functions such as attention, decision-making, and impulse control.
Studies using MRI scans have shown increased thickness and activity in this brain region among experienced meditators, suggesting enhanced cognitive control. This helps explain why mindfulness can improve focus and reduce distractions in daily life.
Mindfulness also reduces activity in the amygdala, the brain’s fear and stress center. By calming this region, mindfulness practice lowers stress levels and emotional reactivity, allowing for greater emotional regulation and resilience.
The National Institute of Mental Health supports the use of mindfulness to modulate stress responses, which is crucial in managing anxiety and depression.
Another important brain area influenced by mindfulness is the hippocampus, which plays a vital role in learning and memory. Regular mindfulness practice has been linked to increased gray matter density in the hippocampus, enhancing memory retention and emotional processing. This connection is highlighted in research published by Psychiatry Research: Neuroimaging.
Beyond structural changes, mindfulness strengthens functional brain networks involved in attention and self-awareness. For instance, the default mode network (DMN), which is associated with mind-wandering and self-referential thinking, shows decreased activity during mindfulness meditation, helping practitioners stay grounded in the present moment.This reduction in mind-wandering is linked to better mental clarity and reduced symptoms of depression.
Scientific studies also demonstrate how mindfulness improves cognitive performance by enhancing working memory capacity and reducing the cognitive load caused by multitasking. A study by University of California, Davis found that mindfulness training helped participants maintain focus longer and perform better on complex tasks.
In summary, mindfulness is a brain superpower because it actively rewires your brain to improve attention, emotional regulation, memory, and stress resilience. These changes empower you to navigate life’s challenges with greater ease and mental clarity, making mindfulness a scientifically backed practice for optimizing brain health.

This infographic highlights the core components of mindful living—like authenticity, intentionality, and grace—proving that mindfulness is a powerful lifestyle, not just a quick fix. It shows how mindfulness rewires our inner world to replace stress with resilience, making it a true superpower for the brain.
Practical Ways to Cultivate Mindfulness Daily
Cultivating mindfulness doesn’t require hours of meditation or retreating from your busy life. In fact, integrating simple mindfulness practices into your daily routine can transform how you experience each moment, improve your focus, and boost your emotional well-being. The key is to start small and build habits that feel natural and sustainable.
One of the easiest ways to begin is by practicing mindful breathing. Taking just a few minutes each day to focus on your breath can calm your nervous system and center your mind.
You can follow guided breathing exercises through popular apps like Headspace or Calm, which offer structured programs designed to reduce stress and enhance focus. These apps also provide tools for beginners to gradually increase their practice time without feeling overwhelmed.
Another effective method is body scan meditation, which involves systematically bringing attention to different parts of your body and noticing sensations without judgment. This practice helps increase bodily awareness and reduce tension and stress.
Mindful walking is a simple way to bring mindfulness into your day, especially if you struggle to sit still. By paying attention to the sensation of your feet touching the ground, the rhythm of your steps, and the sounds around you, you can turn an ordinary walk into a meditative experience.
Eating mindfully is another powerful tool to connect with the present moment. By slowing down and truly savoring your food, noticing flavors, textures, and smells, you not only enhance your eating experience but also improve digestion and reduce overeating.
The Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics provides guidance on mindful eating that can help you develop a healthier relationship with food.
For those with hectic schedules, incorporating short mindfulness moments—sometimes called micro-meditations—can be surprisingly effective. Even 30 seconds of mindful breathing or a quick body awareness check-in between tasks can reset your mental state and reduce stress.
Research from the National Health Service (NHS) highlights how brief mindfulness practices can fit seamlessly into daily life and deliver significant benefits.
Creating reminders to pause and practice mindfulness can also help. Setting alarms on your phone, using mindfulness prompts from apps, or placing sticky notes around your workspace are simple strategies to cultivate consistency. Over time, these small pauses build into a larger habit that strengthens your brain’s ability to stay present.
If you want to deepen your mindfulness practice, consider joining local meditation groups or online courses, such as those offered by the Oxford Mindfulness Centre. This center provides evidence-based training programs. Many universities and wellness centers now offer free or low-cost courses that can provide guidance and community support.
Ultimately, mindfulness is a flexible practice that can be adapted to fit your unique lifestyle. Whether through meditation apps, mindful walking, or simple breathing exercises, regular mindfulness cultivates mental clarity, emotional resilience, and a greater appreciation for life’s moments—making it far from boring and truly a superpower for your brain.
How Mindfulness Transforms Your Life Beyond the Brain
Mindfulness doesn’t just rewire your brain; it creates meaningful changes that ripple across every area of your life, enhancing your relationships, work, and overall well-being. When you practice mindfulness regularly, you become more emotionally intelligent, which improves your ability to empathize and connect with others.
Research from the Greater Good Science Center shows that mindfulness increases compassion and reduces reactive behavior, helping you respond thoughtfully rather than impulsively during conflicts or stressful situations.
In the workplace, mindfulness boosts productivity, creativity, and leadership skills. Companies like Google have incorporated mindfulness training through programs such as Search Inside Yourself, demonstrating how mindfulness fosters focus, resilience, and emotional balance among employees.
The Harvard Business Review highlights how leaders who practice mindfulness tend to make better decisions, manage stress effectively, and cultivate healthier work environments.
Mindfulness also plays a critical role in managing chronic health conditions. Studies compiled by the Mayo Clinic show that mindfulness can alleviate symptoms of chronic pain, lower blood pressure, and improve sleep quality. By helping individuals become more aware of their physical sensations without judgment, mindfulness empowers better self-care and reduces the emotional toll of illness.
Furthermore, mindfulness encourages greater life satisfaction and happiness by fostering gratitude and presence.
According to research published in the Journal of Positive Psychology, people who engage in mindfulness practices report higher levels of positive emotions and lower levels of stress and depression. Mindfulness helps break the cycle of rumination and worry by anchoring your awareness in the present moment, allowing you to savor experiences fully.
The benefits of mindfulness extend to parenting and education as well. Mindful parenting techniques help parents cultivate patience, emotional regulation, and stronger bonds with their children, as supported by findings from the American Psychological Association.
Schools that integrate mindfulness programs report improvements in student attention, behavior, and academic performance. The Mindful Schools organization offers resources and training designed to bring mindfulness into classrooms worldwide.
Lastly, mindfulness supports environmental awareness and sustainability. By nurturing a deeper connection to nature and the present moment, mindfulness inspires eco-conscious behaviors and a sense of stewardship for the planet. Initiatives like the Mindfulness for the Planet movement encourage individuals to adopt mindful living that benefits both personal well-being and the Earth.
In essence, mindfulness is not just a mental exercise but a lifestyle that transforms how you engage with yourself, others, and the world. It cultivates emotional resilience, enhances relationships, supports health, and deepens your connection to life’s richness—making it a truly powerful superpower beyond the brain.
Getting Started with Mindfulness — Tips for Beginners
Starting a mindfulness practice can feel intimidating at first, but it’s easier than many people think. The key is to approach mindfulness with an open mind and a willingness to experiment with different techniques until you find what works best for you.
One helpful way to begin is by setting realistic goals, such as practicing for just five minutes a day, which can gradually build your confidence and consistency. Resources like the Mindful.org Beginner’s Guide provide clear steps and encouragement to ease you into the practice.
Many beginners find guided meditations to be especially supportive. Apps like Insight Timer and Calm offer thousands of free and paid sessions led by experienced teachers, ranging from body scans to loving-kindness meditations. These platforms allow you to explore different styles and lengths of meditation so you can tailor your practice to your lifestyle.
Studies published by JAMA Network support the effectiveness of guided mindfulness meditation in reducing stress and improving mental health.
Creating a dedicated space for mindfulness practice can also enhance your experience. This doesn’t require a special room or expensive equipment—simply choose a quiet spot where you won’t be disturbed, and perhaps add a cushion or a small altar with items that inspire calm and focus.
According to experts at the Oxford Mindfulness Centre, having a consistent practice space helps condition your brain to associate that place with relaxation and presence.
It’s also important to be patient and compassionate with yourself throughout the process. Mindfulness is a skill that develops over time, and it’s normal for your mind to wander or for distractions to arise. The practice is about noticing those moments without judgment and gently bringing your focus back to the present.
Resources like Tara Brach’s guided talks and books provide compassionate guidance on navigating these common challenges.
Finally, joining a mindfulness community can provide valuable support and motivation. Online forums, local meditation groups, and social media communities offer spaces to share experiences, ask questions, and learn from others on the same journey.
Organizations like Mindful Schools and The Mindfulness Network host workshops and events that can deepen your understanding and commitment.
By taking small, consistent steps and utilizing available resources, beginners can build a sustainable mindfulness practice that enhances mental clarity, emotional resilience, and overall well-being—proving that mindfulness is accessible to everyone, not just the “spiritual elite.”
FAQs About Mindfulness Is Not Boring. It’s a Superpower for Your Brain
What is mindfulness?
Mindfulness is the practice of paying full attention to the present moment without judgment. It involves observing your thoughts, feelings, and sensations as they arise.
How does mindfulness benefit the brain?
Mindfulness enhances brain areas related to attention, emotional regulation, and memory. It promotes neuroplasticity, helping the brain form new, healthier neural connections.
Is mindfulness the same as meditation?
Meditation is one way to practice mindfulness, but mindfulness can also be applied informally during everyday activities like walking, eating, or listening.
How long should I practice mindfulness each day?
Starting with 5 to 10 minutes daily is effective. You can gradually increase the duration as you become more comfortable with the practice.
Can mindfulness reduce stress?
Yes, mindfulness reduces stress by lowering activity in the amygdala, the brain’s stress center, and helps you respond calmly to challenging situations.
Is mindfulness scientifically proven?
Numerous studies published in journals like JAMA and Frontiers in Neuroscience confirm mindfulness improves mental health, cognitive function, and emotional well-being.
Do I need to sit still to practice mindfulness?
No, mindfulness can be practiced while walking, eating, or even during daily chores. The key is to focus your attention fully on the current experience.
What are some common mindfulness techniques?
Common techniques include mindful breathing, body scans, mindful walking, and loving-kindness meditation.
Can mindfulness help with anxiety and depression?
Yes, mindfulness-based therapies have been shown to reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression by promoting acceptance and emotional regulation.
Is mindfulness a religious practice?
While mindfulness has roots in Buddhist traditions, it is a secular practice used worldwide for health and well-being, independent of religious beliefs.
How quickly can I see benefits from mindfulness?
Some benefits like reduced stress can be felt after a few sessions, but long-term changes in brain structure and emotional resilience usually develop with consistent practice over weeks or months.
Can children practice mindfulness?
Absolutely. Mindfulness can be adapted for children to improve attention, emotional regulation, and reduce stress in school and home environments.
What is the difference between mindfulness and relaxation?
Relaxation aims to reduce physical tension and stress, while mindfulness is about non-judgmental awareness of the present moment, which may or may not involve relaxation.
Can mindfulness improve sleep?
Yes, mindfulness can improve sleep quality by calming the mind and reducing racing thoughts that interfere with falling asleep.
Are there apps to help me practice mindfulness?
Yes, popular apps like Headspace, Calm, and Insight Timer offer guided meditations and courses suitable for beginners to advanced practitioners.
Is mindfulness effective for pain management?
Mindfulness helps individuals manage chronic pain by changing the way the brain perceives pain signals and reducing emotional distress related to pain.
How do I deal with distractions during mindfulness practice?
It’s normal for the mind to wander. The practice is to gently acknowledge distractions and return your focus to the present moment without self-criticism.
Can mindfulness improve relationships?
Yes, mindfulness fosters empathy, patience, and better communication skills, all of which enhance personal and professional relationships.
Is it possible to practice mindfulness at work?
Definitely. Techniques like mindful breathing or brief body scans can be done discreetly at your desk to increase focus and reduce workplace stress.
Can mindfulness help with addiction recovery?
Mindfulness has been used successfully as part of addiction recovery programs by increasing awareness of cravings and reducing impulsive behaviors.
-Authored By Pragna Chakraborty





