Overactive Minds
Smart students are often praised for their quick thinking, creativity, and problem-solving abilities — but these very traits can make them more prone to distraction. Unlike students who process information linearly, smart individuals tend to think in webs. This tendency, known as divergent thinking, plays a critical role in creativity but can hinder sustained focus on a single task.
From a neurological standpoint, highly intelligent individuals show heightened activity in the default mode network (DMN), a part of the brain associated with internal thought processes like daydreaming, reflection, and future planning.
A meta-analysis in “Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews” found a strong link between DMN activity and attentional lapses, especially in high-functioning individuals.In many cases, smart students themselves are aware of their inability to concentrate, and this awareness leads to frustration.
Instead of fighting their brain’s rapid-fire pattern, smart students can learn to channel their energy more effectively. They can use mindfulness practices such as headspace-guided meditation to help anchor attention when the mind begins to drift.
Perfectionism and Fear of Failure
At first glance, perfectionism may seem like a strength — a desire to produce excellent work and avoid mistakes. But for many smart students, it’s a double-edged sword. The pressure to always excel and meet high expectations can create crippling anxiety that often leads to procrastination and, ironically, distraction.
According to Psychology Today, perfectionists are more likely to delay starting tasks if they fear the outcome won’t meet their own lofty standards.
Distraction, in this case, becomes a coping mechanism. Instead of dealing with the possibility of “failing,” the brain seeks out low-stakes stimuli like scrolling social media or binge-watching content. A 2021 study published in “Computers in Human Behavior” noted that students with perfectionistic traits were more prone to digital distraction and passive avoidance when under academic pressure.
This fear of failure isn’t limited to academics. In high-pressure urban environments where achievement is often linked to self-worth, the mental toll can be severe. Organizations like Earth5R have highlighted how the “burden of expectation” among youth can lead to emotional fatigue and disengagement. In such contexts, distraction becomes a form of escape rather than a simple lack of willpower.
To overcome perfectionism-induced distraction, it’s important to reframe failure as feedback. Many productivity experts also recommend the “imperfect start” method, which involves intentionally beginning tasks without aiming for excellence — just momentum. As explained in this practical guide by Thomas Frank, starting ugly is often better than not starting at all.
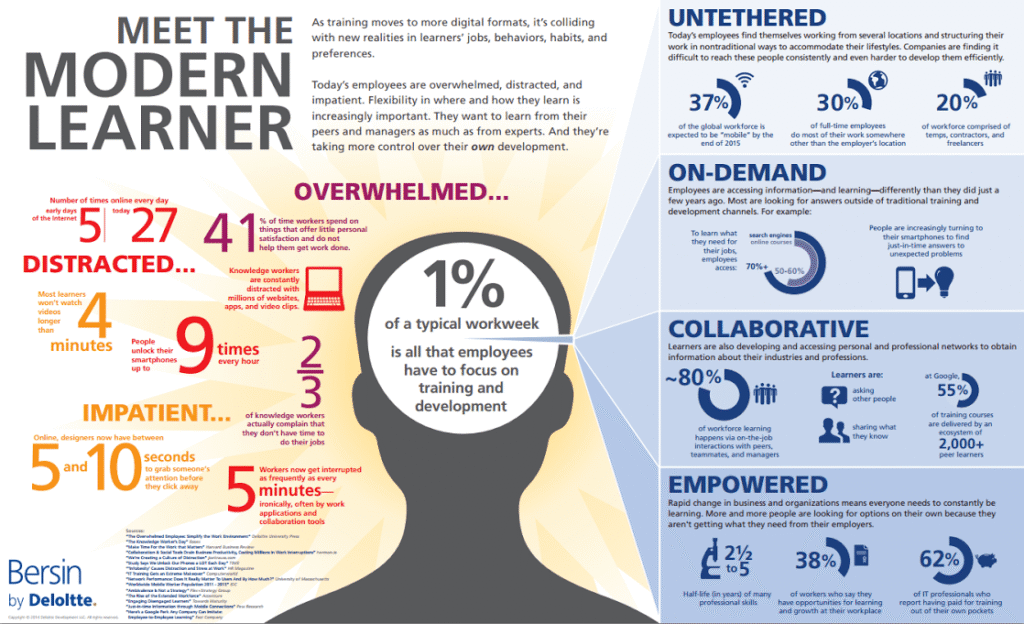
This infographic highlights how modern learners are overwhelmed, distracted, and impatient unlocking their phones 9 times an hour and struggling to focus for more than a few seconds. These insights explain why even smart students lose focus easily in today’s hyper-connected world—and why fixing it starts with rethinking how we engage with learning.
Lack of Challenge or Boredom
One of the most common reasons smart students get distracted is simply because they are bored or under-stimulated. When the material or task at hand doesn’t challenge their intellect, their minds naturally seek excitement elsewhere.
According to educational psychologists, boredom arises when there’s a mismatch between a student’s skill level and the difficulty of the task. This imbalance often leads to mental disengagement and wandering attention, as the brain craves stimulation that the current activity fails to provide.
Research published by the “American Psychological Association” shows that boredom is linked to decreased motivation and increased distractibility in academic settings. This phenomenon is especially prominent in gifted students who crave cognitive complexity and novel problem-solving opportunities, making routine or repetitive assignments feel tedious.
Teachers and parents can unintentionally contribute to this by not providing sufficiently challenging or varied learning experiences. According to Edutopia, incorporating differentiated instruction and project-based learning can significantly reduce boredom by allowing students to explore topics at their own pace and interest level.
Finally, boredom can sometimes mask underlying issues such as lack of purpose or connection to the subject matter. When smart students don’t see the relevance of what they’re learning, their attention falters.
Studies suggest that linking academic content to real-world applications and personal interests boosts engagement and reduces distraction. For instance, incorporating experiential learning techniques like simulations, internships, or community projects can help students find meaning in their work and sustain their focus.
Digital Distractions and Multitasking
In today’s hyperconnected world, digital distractions are one of the biggest culprits behind why even the smartest students struggle to maintain focus. Smartphones, social media, instant messaging, and endless streams of notifications constantly compete for attention.
According to research highlighted by Earth5R, the average person checks their phone over 150 times a day, breaking concentration and fragmenting attention spans. For smart students who rely on mental clarity, these interruptions can severely disrupt their ability to engage deeply with academic work.
Moreover, the habit of multitasking — attempting to juggle multiple tasks simultaneously — is particularly common among high-achieving students who feel pressured to be productive at all times.
However, numerous studies, including one reviewed on Medium, show that multitasking actually reduces efficiency and increases error rates. The brain isn’t designed to switch rapidly between tasks without losing focus and cognitive energy. This “switch cost” can make smart students feel mentally exhausted, ironically lowering their overall productivity.
Digital distractions also activate the brain’s reward system through dopamine releases, making it tempting to check social media or messages even when the intention is to focus. A study from “The Journal of Neuroscience” explains how this intermittent reward loop conditions users to seek constant stimulation, reinforcing distraction habits.
This effect is detailed in articles like this one from Psychology Today, which discusses how technology hijacks our attention by tapping into basic neurological mechanisms.
For smart students, whose minds are often wired to seek complexity and novelty, these quick digital hits can become even more alluring. It’s easy to fall into a cycle of checking notifications, quickly losing track of time and shifting away from deeper learning.
Strategies like the “Pomodoro Technique” or using apps to block distracting websites can help. As Earth5R notes, digital detoxes and intentional tech use are essential habits to cultivate better focus and mental wellbeing.
Finally, parents, educators, and students themselves must recognize that managing digital distractions is not just about willpower. It involves creating mindful tech habits, setting boundaries, and understanding how technology impacts cognition. This balanced approach is well summarized in this Medium article on mindful technology use, which offers practical advice for reclaiming focus without sacrificing the benefits of modern tools.
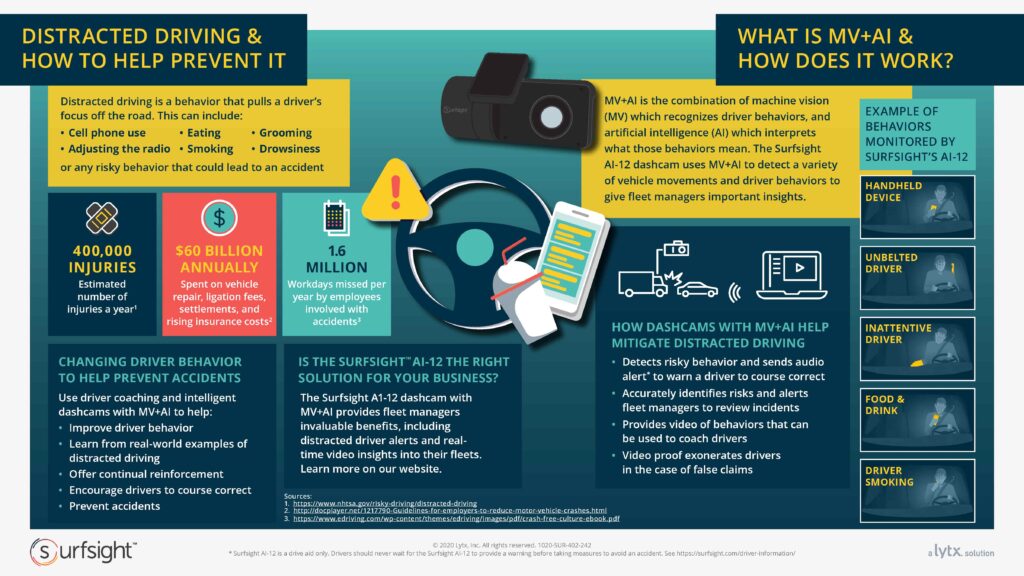
This infographic shows how distractions—like phones, eating, or drowsiness—can lead to dangerous driving errors, mirroring how smart students lose focus due to constant mental interruptions. Just as AI tools help drivers stay alert, students need structured strategies and tools to recognize and manage distractions effectively.
Strategies to Regain Focus and Improve Concentration
Regaining focus is a skill smart students can develop by adopting intentional habits and practical techniques.
Time Management Techniques That Work
One effective method involves structured time management, such as the Pomodoro Technique, which breaks work into focused intervals followed by short breaks. Studies show this approach helps sustain concentration and reduce burnout. Earth5R emphasizes how time-blocking and scheduling can train the brain to focus during specific windows, improving productivity overall. You can learn more about it here on Earth5R.
Mindfulness and Meditation for Focus
Another powerful strategy is cultivating mindfulness and meditation practices. Mindfulness helps students become aware of their wandering attention and gently bring it back to the present task.
Creating a Distraction-Free Workspace
Smart students can also benefit from environmental design—optimizing their workspace to minimize distractions. This includes decluttering, controlling noise levels, and using tools like noise-cancelling headphones or ambient sound apps.
Breaking Tasks Into Manageable Chunks
Breaking tasks into smaller, manageable chunks can combat overwhelm and perfectionism-related distractions. This method, often called “chunking,” allows students to experience progress frequently, boosting motivation.
The Power of Goal Setting
Setting clear goals and priorities plays a crucial role in focus enhancement. SMART goals (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) guide students to focus on what truly matters and avoid irrelevant distractions.
Together, these strategies form a holistic approach to overcoming distraction and maximizing the cognitive strengths of smart students. The key is consistent practice and self-compassion during the journey toward improved focus.
The Role of Emotional and Mental Health
Emotional and mental health plays a critical role in a student’s ability to maintain focus and avoid distraction. High-achieving students often experience significant stress, anxiety, and even depression due to the intense pressure to perform.
According to Earth5R’s research on youth mental wellness, unmanaged stress can impair cognitive functions such as memory and attention, making concentration much harder to sustain during academic tasks. Anxiety, in particular, is a common challenge among smart students, who may set impossibly high standards for themselves.
Studies published by “The Anxiety and Depression Association of America” show that anxiety can cause the brain to fixate on worries, pulling focus away from the task at hand and leading to what many describe as “mind fog” or mental clutter.
Depression also significantly affects attention and motivation. A report from the “National Institute of Mental Health” highlights that depressive symptoms often include difficulty concentrating and lack of energy, which can make even simple tasks feel overwhelming.
Recognizing these signs early is essential for smart students who may otherwise mask their struggles behind academic excellence. Resources like Mental Health America provide valuable guidance for students seeking help.
Peer support and open conversations about mental health also reduce stigma and create safe spaces for students to share challenges. Platforms like Medium’s mental health community foster dialogue and offer stories of overcoming distraction caused by emotional struggles, inspiring others to seek help and adopt healthier coping strategies.
The Myth of Constant Productivity
Smart students often internalize the belief that they must be productive at all times — that every moment not spent studying or building their resume is wasted. This mindset, driven by hustle culture and unrealistic academic expectations, leads to chronic stress and a dangerous cycle of burnout.
According to Harvard Business Review, continuous work without breaks diminishes both the quality of output and the ability to focus. The brain functions best in cycles of deep work followed by intentional rest. Ignoring this rhythm can result in decision fatigue, irritability, and a sharp decline in creativity — all of which undermine long-term academic success.
Earth5R advocates for a balanced approach to personal development, noting that rest, play, and wellness are integral to sustainable learning. Incorporating breaks, hobbies, and downtime isn’t laziness — it’s essential for replenishing mental energy and staying motivated. Recognizing that value isn’t solely measured in productivity helps students redefine success and build a healthier, more focused lifestyle.
FAQs on Why Smart Students Get Distracted Easily (And How to Fix It)
Why do smart students get distracted easily?
Smart students often get distracted due to boredom, perfectionism, digital interruptions, or emotional stress, which can interfere with sustained focus.
Is boredom a common cause of distraction among intelligent students?
Yes, when tasks are not challenging enough, smart students’ minds seek stimulation elsewhere, leading to distraction.
How does perfectionism contribute to distraction?
Perfectionism can cause fear of failure and procrastination, making it harder to concentrate on tasks.
Can digital devices really affect a student’s focus that much?
Absolutely. Constant notifications and the temptation of social media trigger dopamine responses, making it difficult to maintain attention.
What is chunking and how does it help focus?
Chunking is breaking down large tasks into smaller, manageable pieces, which reduces overwhelm and helps maintain motivation.
How do mindfulness and meditation improve concentration?
They train the brain to recognize wandering thoughts and gently bring focus back to the present task.
What role does goal setting play in improving focus?
Setting clear, specific goals helps prioritize tasks and avoid distractions by providing direction and motivation.
Can emotional stress impact a student’s ability to focus?
Yes, stress, anxiety, and depression can impair cognitive functions, making it harder to concentrate.
How can a distraction-free workspace boost productivity?
A clean, organized environment minimizes external interruptions and creates a mental space conducive to focus.
Are breaks important when trying to focus?
Yes, regular breaks help recharge the brain, improving long-term concentration and preventing burnout.
Why do smart students sometimes procrastinate?
Procrastination can stem from fear of failure, perfectionism, or feeling overwhelmed by a task’s complexity.
Is multitasking effective for studying?
No, multitasking reduces efficiency and focus because the brain switches between tasks instead of concentrating on one.
How can students manage digital distractions?
Strategies include turning off non-essential notifications, using focus apps, and setting dedicated study times.
Does lack of interest in a subject cause distraction?
Yes, when students don’t find the material relevant or engaging, their attention tends to wander.
How does self-compassion help improve focus?
Being kind to oneself reduces anxiety and perfectionism, making it easier to maintain motivation and concentration.
What are the signs that mental health is affecting focus?
Symptoms may include difficulty concentrating, fatigue, irritability, and withdrawal from activities.
Can physical exercise improve cognitive focus?
Yes, regular exercise increases blood flow to the brain and boosts mood, both of which support better concentration.
How important is sleep for maintaining attention?
Adequate sleep is critical as it helps consolidate memory and refreshes the brain for optimal focus.
What is the impact of nutrition on focus and attention?
A balanced diet supports brain function, while excessive sugar and caffeine can cause energy crashes and distractibility.
How can students stay motivated during long study sessions?
Using goal setting, rewards, breaks, and varied study techniques can maintain engagement and reduce distractions.
-Authored By Pragna Chakraborty





